- All
- Technical Dictionary
- Production Process
Technical Dictionary
Sputtering
Sputtering works by performing ion bombardment on targets using plasma and knocking the atoms off the surface of targets. These atoms are ejected in a gaseous form, and then grow into a film on substrates through adhesion, adsorption, surface migration and nucleation.Sputtering principle
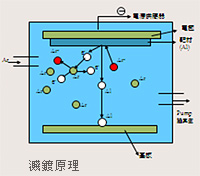 The inert gas of argon is directed into an enclosed vacuum chamber. A high voltage is applied between the surface of target and the substrate. This voltage ionizes the argon gas into argon ions (Ar+). At this moment, the argon ions (Ar+) are accelerated to the cathode to bombard the target surface. The atoms and secondary electrons on the target surface break loose, and the target atoms move to the surface of substrates to form a thin layer of film, while the secondary electrons are accelerated to the anode to create more ionized argon.
The inert gas of argon is directed into an enclosed vacuum chamber. A high voltage is applied between the surface of target and the substrate. This voltage ionizes the argon gas into argon ions (Ar+). At this moment, the argon ions (Ar+) are accelerated to the cathode to bombard the target surface. The atoms and secondary electrons on the target surface break loose, and the target atoms move to the surface of substrates to form a thin layer of film, while the secondary electrons are accelerated to the anode to create more ionized argon.
Magnetron of sputteirng
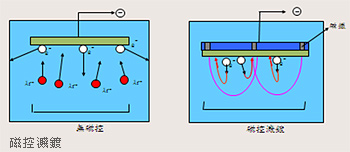 A magnetron device is installed at the sputtering source (cathode). The electromagnetic force generated from the electromagnetic effects between magnetic field and electric field has influence on the movement of electrons in the plasma, causing the electron to go into a spiral movement. Due to the intervention of magnetic field, the electrons no longer move in a linear fashion. The spiral movement causes the electrons to move a longer distance before the plasma dissipates, thus increasing the number of impacts between electrons and gas molecules and in turn the possibility of ionized gas molecules. More ions are created this way to impact the targets, and more target atoms are sputtered out and deposited on substrates. Therefore, the source of magnetron of sputtering (cathode) will increase the coating rate dramatically during sputtering.
A magnetron device is installed at the sputtering source (cathode). The electromagnetic force generated from the electromagnetic effects between magnetic field and electric field has influence on the movement of electrons in the plasma, causing the electron to go into a spiral movement. Due to the intervention of magnetic field, the electrons no longer move in a linear fashion. The spiral movement causes the electrons to move a longer distance before the plasma dissipates, thus increasing the number of impacts between electrons and gas molecules and in turn the possibility of ionized gas molecules. More ions are created this way to impact the targets, and more target atoms are sputtered out and deposited on substrates. Therefore, the source of magnetron of sputtering (cathode) will increase the coating rate dramatically during sputtering.
Plasma
 Plasma is a mass of partially ionized gas consisting of ions, electrons, molecules and atomic groups. Plasma is generated by applying high voltage between electrodes at a very low pressure (l00mTorr~a few mTorr). A high electric field is created between these electrodes. The gaseous, positively charged ions between the electrodes are accelerated to bombard the surface of the negatively charged cathode, thus generating many different particles including secondary electrons. These secondary electrons broken loose in the bombardment are accelerated by the electric field and moving toward the positively charge electrode. En route, multiple collisions are created with other gaseous particles between the electrodes, thus generating ionization or excitation. As mentioned above, the ionized particles are given tremendous amount of energy under the acceleration of electric field, and directed to bombard the surface of cathode plate, thus generating secondary electrons. As a result, the relationship between the ions and electrons between the 2 electrodes just keep going and going like a chain reaction of breakdown that produces large quantity of ions and electrons in low pressure, and in turn plasma. Plasma consists of positively charged ions, negatively charged electrons and neutral atoms, and therefore constantly remains electrically neutral.
Plasma is a mass of partially ionized gas consisting of ions, electrons, molecules and atomic groups. Plasma is generated by applying high voltage between electrodes at a very low pressure (l00mTorr~a few mTorr). A high electric field is created between these electrodes. The gaseous, positively charged ions between the electrodes are accelerated to bombard the surface of the negatively charged cathode, thus generating many different particles including secondary electrons. These secondary electrons broken loose in the bombardment are accelerated by the electric field and moving toward the positively charge electrode. En route, multiple collisions are created with other gaseous particles between the electrodes, thus generating ionization or excitation. As mentioned above, the ionized particles are given tremendous amount of energy under the acceleration of electric field, and directed to bombard the surface of cathode plate, thus generating secondary electrons. As a result, the relationship between the ions and electrons between the 2 electrodes just keep going and going like a chain reaction of breakdown that produces large quantity of ions and electrons in low pressure, and in turn plasma. Plasma consists of positively charged ions, negatively charged electrons and neutral atoms, and therefore constantly remains electrically neutral.
Dry Etching
1. Physical etching: (1) Sputter Etching (2) Ion Beam Etching
2. Chemical etching: Plasma Etching
3. Physical and chemical composite etching: Reactive Ion Etching (RIE)
Production Process
PVD process for injection products :
Plastic Injection Ultrasonic Cleaning Drying Base coat Vacuum coating Top coat QC check Packaging ShippingPVD process for glass products :
Glass Supersonic(Ultrasonic) cleaning Drying Vacuum coating QC check Packaging ShippingCategories
Decoration coating
- Reflective Coating
- Translucent reflective coating
Function coating
- EMI Film
- Optical Film
Application:AR , Decoration - Conductive Film
- T.C.O Film
- Anti Finger
- Anti-smudge
- NCVM
Ingredients
1. Metal
- Al;Cu;Sus..
2. Non-metal
- PC;PET;PMMA;PI;Nylon;FR4;PPO;PPS;PPA;Glass;Wafer;LCP;PU;TPU;TPE; ABS;ABS+PC;PMMA+PC..